
It's Heart Awareness Month
Posted on Monday, 10 February 2025 under Wellness,
Did you know almost 1 in 3 New Zealand deaths are caused by cardiovascular disease?
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women. Heart attacks do not discriminate – women are just as likely to have a heart attack as men are. But women are more likely to die from one.
What's interesting though, is that men and women may have different symptoms. Ensure you're familiar with the differences:
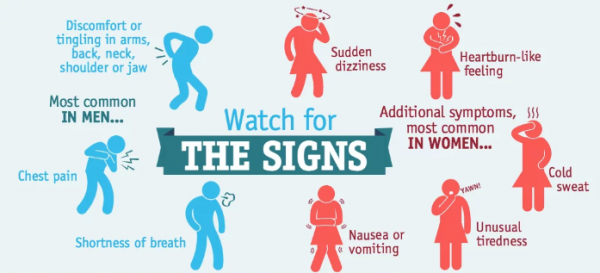
A heart attack (myocardial infarction) happens when blood stops flowing to part of your heart. Find out about heart attack causes, what you can do to recognise a heart attack and speed your recovery.
A heart attack happens when blood stops flowing to part of your heart muscle. Unless blood flow is restored quickly, this can result in permanent heart damage.
Do you know the difference between a heart attack and a stroke?
Common heart disorders can increase the risk of stroke. For example, coronary artery disease increases the risk because plaque builds up in the arteries and blocks the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the brain.
When the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, causing a part of the brain to die, it's called a stroke, or "brain attack". Stroke is similar to a heart attack, but it affects the blood vessels in the brain instead of the heart.
During a stroke, the cells in the affected part of the brain start to die and that part of the brain cannot work properly. This can affect a person's ability to walk, talk, eat, see, read, socialise, or do things they were able to do before the stroke.
Many people with stroke may also have fatigue or problems with remembering, understanding, or thinking properly.
A stroke is a very serious medical event, but many people go on to recover and live healthy lives - particularly when signs or symptoms of stroke are identified and early medical intervention is achieved.
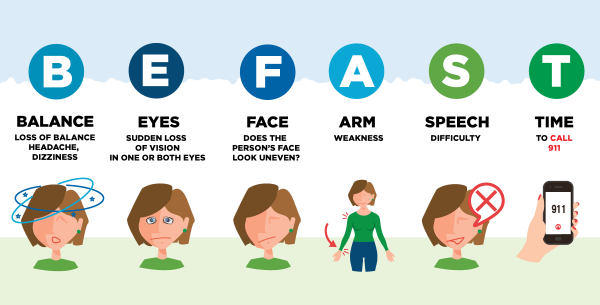 It's vital to recognise when someone is having a stroke and to start treatment as soon as possible, because the sooner medical treatment begins, the more likely brain damage can be reduced and a better outcome achieved. The quicker a clot can be dissolved or removed, the less damage is done, and the better the chance of a strong recovery.
It's vital to recognise when someone is having a stroke and to start treatment as soon as possible, because the sooner medical treatment begins, the more likely brain damage can be reduced and a better outcome achieved. The quicker a clot can be dissolved or removed, the less damage is done, and the better the chance of a strong recovery.

